Insider threats: The enemy within
October 9, 2023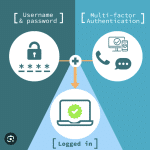
What is Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)?
October 12, 2023Small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) are increasingly becoming targets of cyber espionage. Cyber espionage is a type of cyberattack in which an unauthorized user attempts to access sensitive or classified data or intellectual property (IP) for economic gain, competitive advantage, or political reasons.
SMBs are particularly vulnerable to cyber espionage because they often lack the resources and expertise to implement robust cybersecurity measures. Additionally, SMBs often have valuable IP and trade secrets that are attractive to cyber attackers.
Cyber espionage can have a devastating impact on SMBs. It can lead to the loss of sensitive data, such as customer information, financial data, and trade secrets. It can also damage an SMB’s reputation and make it difficult to attract new customers and partners.
In some cases, cyber espionage can even lead to the closure of an SMB. A 2022 study by the Small Business Administration found that 60% of SMBs that experience a cyberattack go out of business within six months.
Here are some of the ways that cyber espionage can affect SMBs:
- Loss of sensitive data: Cyber attackers may steal sensitive data from SMBs, such as customer information, financial data, and trade secrets. This data can then be used for identity theft, fraud, or to gain a competitive advantage.
- Damage to reputation: A cyberattack can damage an SMB’s reputation and make it difficult to attract new customers and partners. Customers may be reluctant to do business with an SMB that has been hacked, and partners may be hesitant to share sensitive information with them.
- Financial losses: Cyberattacks can lead to financial losses for SMBs. SMBs may have to pay to recover from the attack, and they may also lose revenue due to lost customers and disrupted operations.
- Interruption of operations: Cyberattacks can disrupt an SMB’s operations, making it difficult to do business. For example, a cyber attacker may launch a ransomware attack that encrypts the SMB’s data, making it inaccessible.
- Closure: In some cases, cyber espionage can lead to the closure of an SMB. A 2022 study by the Small Business Administration found that 60% of SMBs that experience a cyberattack go out of business within six months.
Here are some tips for SMBs to protect themselves from cyber espionage:
- Implement a cybersecurity policy: SMBs should implement a cybersecurity policy that outlines their security procedures and employee training requirements.
- Use strong passwords and multi-factor authentication: SMBs should require their employees to use strong passwords and multi-factor authentication for all access to company systems and data.
- Keep software and systems up to date: SMBs should keep their software and systems up to date with the latest security patches.
- Educate employees about cybersecurity best practices: SMBs should educate their employees about cybersecurity best practices, such as how to identify and report phishing emails.
- Invest in cybersecurity solutions: SMBs should invest in cybersecurity solutions, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and antivirus software.
SMBs can also protect themselves from cyber espionage by working with a managed security service provider (MSSP). An MSSP can provide SMBs with the expertise and resources they need to implement and maintain robust cybersecurity measures.
If you are an SMB owner, it is important to take steps to protect your business from cyber espionage. By implementing the tips above, you can reduce your risk of being attacked and minimize the impact of an attack if it does occur.
Here are some additional tips for SMBs to protect themselves from cyber espionage:
- Be careful about what information you share online: SMBs should be careful about what information they share online, both on their website and on social media. Avoid sharing sensitive information, such as customer lists, financial data, and trade secrets.
- Monitor your systems for suspicious activity: SMBs should monitor their systems for suspicious activity, such as unusual login attempts or unauthorized access to files.
- Have a plan in place for responding to a cyberattack: SMBs should have a plan in place for responding to a cyberattack. This plan should include steps for notifying customers and partners, containing the attack, and recovering from the attack.
By taking these steps, SMBs can reduce their risk of becoming victims of cyber espionage and protect their businesses from the devastating consequences of an attack.
#CyberEspionage #SMBs #Cybersecurity