Threat, Vulnerability, and Risk: Understanding the Cybersecurity Trifecta
December 24, 2024
Protecting Your Digital Life: Choosing the Best Cybersecurity Software for Personal Use
December 28, 2024In the high-stakes world of cybersecurity, where attackers are constantly probing for weaknesses, defenders need to be innovative and proactive. One such clever tactic is the use of honeypots. These ingenious tools serve as decoys, luring attackers away from valuable assets while providing defenders with crucial insights into their methods. As your trusted cybersecurity partner, Krypto IT wants to demystify honeypots, explain how they work, and outline best practices for deploying them effectively.
What is a Honeypot?
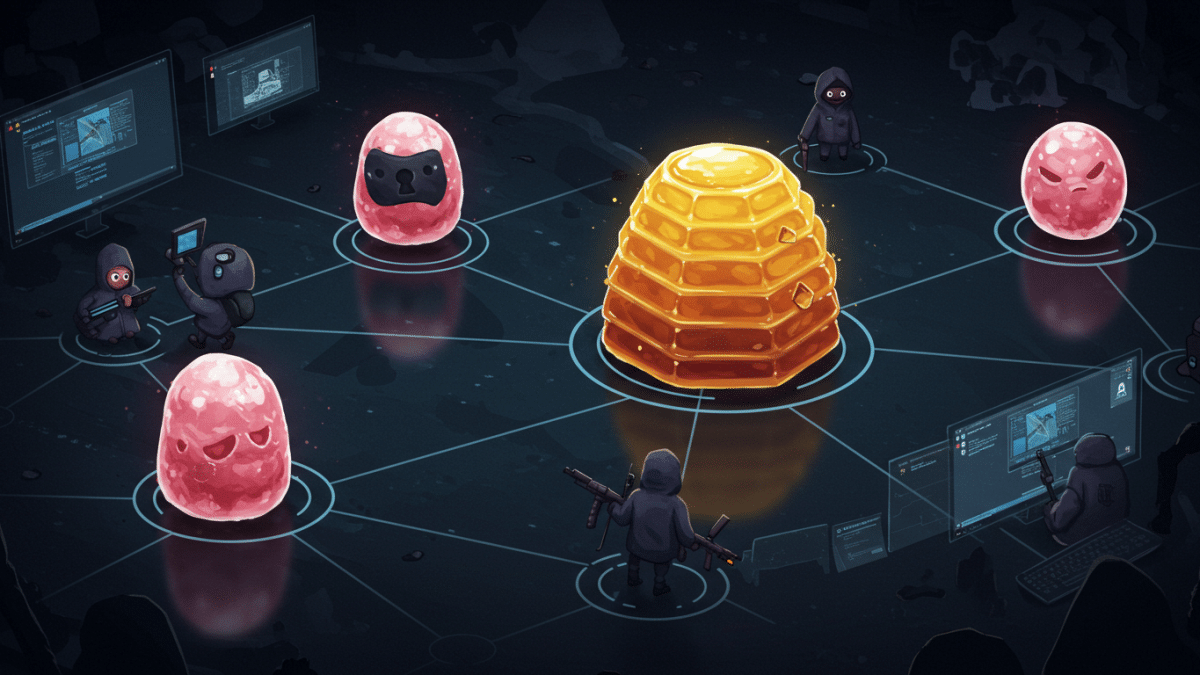
A honeypot is a security mechanism that creates a controlled, isolated environment designed to mimic a legitimate system or network. It’s essentially a trap set to attract and detect unauthorized activity. Think of it like a fake storefront in a sting operation – it looks real to the unsuspecting criminal, but it’s actually under surveillance by law enforcement.
Honeypots can take various forms, including:
- Fake servers: These can emulate web servers, file servers, or database servers.
- Fake applications: These can mimic vulnerable applications known to be targeted by attackers.
- Fake data: These can be files or databases that appear to contain sensitive information but are actually fabricated.
- Fake network segments: Creating an isolated network segment made to appear like a valuable part of your infrastructure.
How Do Honeypots Work?
The primary goal of a honeypot is to deceive attackers into interacting with it instead of the real target. By doing so, the honeypot serves several critical functions:
- Detection: Honeypots are designed to detect unauthorized access attempts and malicious activity. Any interaction with a honeypot is considered suspicious because legitimate users should have no reason to access it.
- Alerting: When an attacker interacts with a honeypot, it triggers alerts, notifying security teams of the intrusion attempt.
- Information Gathering: Honeypots collect valuable data about the attacker’s tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs), including their IP address, tools used, and attack methods. This information can be used to improve defenses and understand the evolving threat landscape.
- Delaying the Attacker: While the attacker is engaged with the honeypot, they are diverted from the actual target, giving security teams time to respond and potentially prevent a real breach.
- Learning and Research: The data collected by honeypots can be used for research, threat intelligence, and the development of new security measures.
Types of Honeypots
Honeypots are generally categorized based on their level of interaction and complexity:
- Low-interaction honeypots: These simulate only a limited number of services and applications. They are easier to deploy and maintain but provide less information about the attacker. They primarily serve to detect and log attacks.
- High-interaction honeypots: These provide a more realistic and complex environment, often running real operating systems and applications. They offer deeper insights into attacker behavior but require more resources and expertise to manage. They carry higher risk of being compromised and used to attack other systems if not probably contained.
- Research honeypots: These are typically high-interaction honeypots used by security researchers and organizations to study attacker behavior and develop new security solutions.
- Production honeypots: These are deployed within an organization’s production network to detect and respond to attacks that have bypassed other security measures.
Best Practices, Policies, and Procedures for Honeypot Deployment
1. Planning and Policy:
- Define Objectives: Clearly define the goals of deploying a honeypot. What do you hope to achieve? What type of threats are you targeting?
- Develop a Policy: Create a formal honeypot policy that outlines the purpose, scope, deployment, monitoring, and response procedures.
- Legal Considerations: Consult with legal counsel to ensure compliance with relevant laws and regulations regarding data collection and privacy.
- Risk Assessment: Conduct a risk assessment to identify potential risks associated with deploying a honeypot and develop mitigation strategies.
2. Deployment:
- Placement: Strategically place the honeypot where it is likely to attract attackers but is isolated from critical systems.
- Configuration: Configure the honeypot to mimic real systems and services relevant to your organization, but ensure that it does not contain any actual sensitive data.
- Isolation: Isolate the honeypot from your production network to prevent attackers from using it as a stepping stone to other systems. Use firewalls, VLANs, and other network segmentation techniques.
- Hardening: Secure the underlying operating system and applications running on the honeypot to prevent it from being completely compromised.
3. Monitoring and Alerting:
- Centralized Logging: Configure the honeypot to log all activity to a centralized logging server for analysis.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Implement real-time monitoring and alerting mechanisms to detect and respond to suspicious activity promptly.
- Alerting Thresholds: Define clear alerting thresholds based on the type and severity of activity observed on the honeypot.
4. Response:
- Incident Response Plan: Integrate honeypot alerts into your existing incident response plan.
- Investigation: When an alert is triggered, investigate the activity to determine the nature of the threat and the attacker’s intentions.
- Containment: If necessary, take steps to contain the attacker’s activity within the honeypot and prevent further spread.
- Analysis: Analyze the collected data to extract valuable threat intelligence, such as the attacker’s IP address, tools, and techniques.
- Reporting: Document all honeypot activity, including alerts, investigations, and findings.
5. Maintenance:
- Regular Updates: Keep the honeypot’s operating system, applications, and security tools up to date with the latest patches.
- Review and Refinement: Regularly review and refine your honeypot strategy based on the data collected and lessons learned.
Krypto IT: Your Partner in Proactive Cybersecurity
Honeypots are a powerful tool for proactive threat detection and intelligence gathering. They provide a unique window into the minds of attackers, helping organizations stay one step ahead of evolving threats.
Krypto IT can help you design, deploy, and manage a honeypot solution tailored to your specific needs. Our experts can guide you through the entire process, from planning and policy development to deployment, monitoring, and incident response. Contact us today for a free consultation and let us help you enhance your cybersecurity posture with the strategic use of honeypots.
Don’t just react to threats. Anticipate them. Be proactive. Be secure with Krypto IT.
#Cybersecurity #Honeypot #ThreatDetection #CyberThreatIntelligence #InfoSec #CyberDefense #ProactiveSecurity #IncidentResponse #NetworkSecurity #KryptoIT #SecuritySolutions #CyberAwareness #DigitalSecurity #ThreatHunting #SecurityStrategy