New Spyware Threatens SMBs: Stay Protected
March 6, 2025
Human Error: Cyber’s Weakest Link
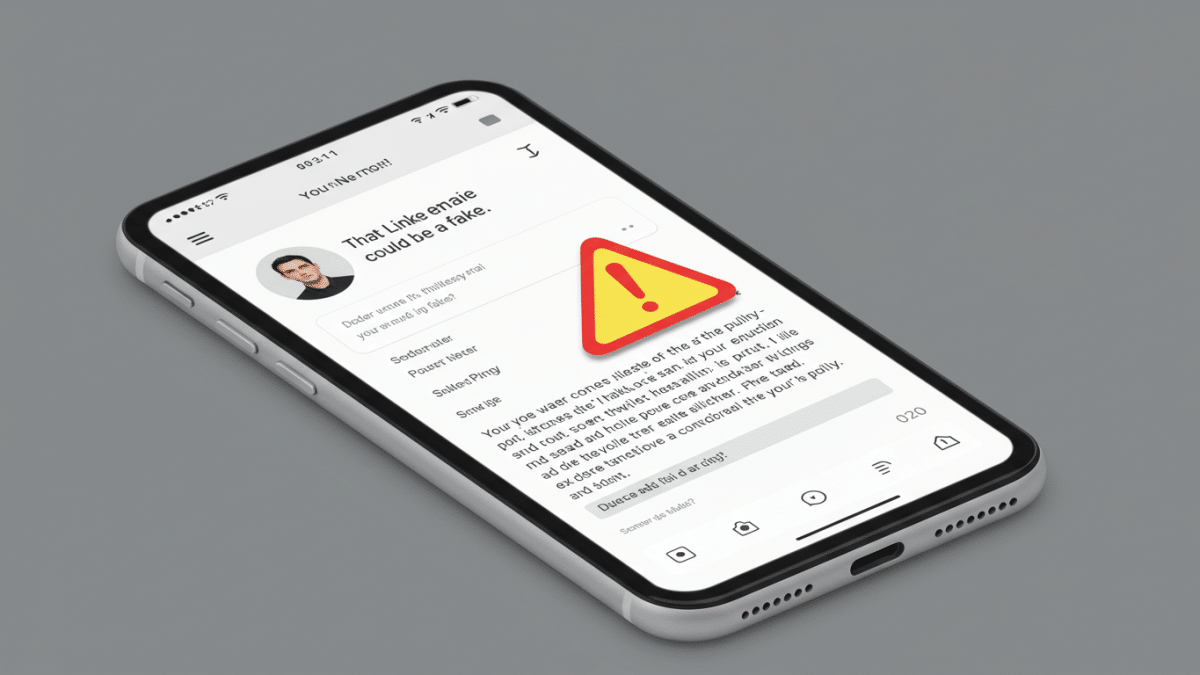
March 9, 2025Is That LinkedIn Email Real? Cyber Threats Target SMBs
In today’s interconnected world, LinkedIn has become an indispensable tool for networking, recruitment, and business development. However, this professional platform is increasingly targeted by cybercriminals looking to exploit its vast user base. As highlighted in recent reports, including the article “Watch out – that LinkedIn email could be a fake, laden with malware,” phishing attacks disguised as legitimate LinkedIn communications are on the rise, posing a significant threat to small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) in Houston and beyond.
The Growing Threat of LinkedIn Phishing
Cybercriminals are becoming increasingly sophisticated in their tactics. They craft emails that mimic official LinkedIn notifications, often using compelling subject lines that urge recipients to take immediate action. These emails may contain links to malicious websites or attachments laden with malware, designed to steal sensitive data or compromise your systems.
For SMBs, the consequences of falling victim to a LinkedIn phishing attack can be devastating. These attacks can lead to:
- Data breaches: Sensitive customer information, financial data, and proprietary business secrets can be stolen.
- Financial losses: Ransomware attacks can lock down critical systems, demanding hefty ransoms for data recovery.
- Reputational damage: A security breach can erode customer trust and damage your company’s reputation.
- Operational disruptions: Malware can disrupt daily operations, leading to downtime and lost productivity.
Protecting Your SMB from LinkedIn Phishing
As a Houston-based cybersecurity company, Krypto IT understands the unique challenges faced by SMBs. Here are some essential best practices to protect your business from LinkedIn phishing attacks:
- Educate Your Employees:
- Regularly train your staff on how to identify phishing emails and other social engineering tactics.
- Emphasize the importance of verifying the sender’s email address and scrutinizing links before clicking.
- Simulate phishing attacks to test employee awareness and identify areas for improvement.
- Implement Strong Email Security:
- Use email filtering and anti-phishing software to block suspicious emails.
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all email accounts to add an extra layer of security.
- Setup SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records to help prevent email spoofing.
- Verify Links and Attachments:
- Hover over links to check the destination URL before clicking.
- Avoid downloading attachments from unknown or suspicious senders.
- If a link looks suspicious, go directly to the known website rather than clicking the link.
- Strengthen LinkedIn Security:
- Enable MFA for all LinkedIn accounts.
- Regularly review your LinkedIn security settings.
- Be cautious about accepting connection requests from unknown individuals.
- Maintain Up-to-Date Software:
- Ensure all software, including operating systems and antivirus programs, is updated with the latest security patches.
- Regularly scan systems for malware and vulnerabilities.
- Incident Response Plan:
- Develop a comprehensive incident response plan that outlines the steps to take in the event of a security breach.
- Regularly test and update the plan to ensure its effectiveness.
Krypto IT: Your Houston Cybersecurity Partner
At Krypto IT, we specialize in providing comprehensive cybersecurity solutions for SMBs in the Houston area. We understand the unique threats you face and offer tailored services to protect your business from evolving cyber risks.
Don’t wait until it’s too late. Protect your business from LinkedIn phishing and other cyber threats. Contact Krypto IT today for a free cybersecurity consultation. We’ll assess your current security posture and provide recommendations to strengthen your defenses.
Contact Us:
713-526-3999
#Cybersecurity #SMB #Houston #Phishing #LinkedIn #DataSecurity #ITSecurity #KryptoIT #TechTips #SmallBusiness #CyberAwareness #Malware