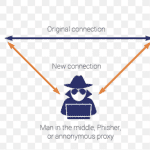
Man in the Middle Attacks: How to Protect Yourself
November 29, 2023
Preparing for the Inevitable: Building Resilient Cybersecurity Strategies for the Future
December 3, 2023In today’s interconnected world, passwords have become our digital keys, granting access to our online lives. From email accounts to social media profiles, financial institutions to healthcare records, our passwords protect a wealth of sensitive information. However, as our reliance on passwords grows, so does the risk of password attacks. Hackers are constantly devising new methods to steal passwords, making it crucial to implement strong password policies and educate users about password security.
What are Password Policies?
Password policies are sets of guidelines and rules that define password requirements and usage practices within an organization or system. These policies aim to enhance password security by mandating strong passwords, enforcing regular password changes, and restricting password reuse.
Key Elements of Strong Password Policies:
- Minimum Password Length: Mandate longer passwords, as shorter passwords are easier to crack. Aim for a minimum password length of 12 characters.
- Password Complexity: Require a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. This increases the entropy of passwords, making them more difficult to guess or crack.
- Password Expiration and Rotation: Enforce periodic password changes to reduce the risk of prolonged exposure in case of a breach. Recommend password changes every 60-90 days.
- Password Reuse Prevention: Prohibit the reuse of passwords across different accounts and systems. This prevents compromised passwords from granting access to multiple accounts.
- Account Lockouts: Implement account lockout mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access attempts from escalating. After a certain number of failed attempts, lock the account for a set period.
- Password History: Maintain a history of previously used passwords to prevent users from reusing compromised credentials. This adds an extra layer of protection against password reuse attacks.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implement MFA as an additional layer of security beyond passwords. MFA requires additional verification factors, such as a code sent to a mobile phone, to gain access.
Common Password Attacks and Prevention:
- Brute Force Attacks: Hackers attempt to guess passwords by systematically trying all possible combinations. Strong passwords and account lockouts can mitigate this threat. Use a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters to increase the complexity and make it harder for hackers to guess.
- Credential Stuffing: Hackers use stolen credentials from one site to attempt access to other accounts. Unique passwords for each account prevent credential stuffing. Create unique passwords for each account you use, avoiding the reuse of passwords across multiple platforms.
- Phishing Attacks: Hackers trick users into revealing their passwords through deceptive emails or websites. Educate users about phishing tactics and encourage them to report suspicious emails. Be cautious when opening emails or clicking on links, especially those from unknown senders. Verify the legitimacy of websites before entering your login credentials.
- Malware Attacks: Malware can steal passwords stored on devices or intercept passwords as they are entered. Install antivirus and anti-malware software and avoid clicking on suspicious links or attachments. Keep your antivirus and anti-malware software up to date to protect against the latest threats.
- Social Engineering Attacks: Hackers manipulate users into revealing passwords or other sensitive information through social interactions. Educate users about social engineering techniques and encourage them to be cautious about sharing personal information online. Be wary of unsolicited social media messages or calls that attempt to extract personal information.
Additional Password Security Tips:
- Avoid using personal information, such as your name, birthday, or address, in your passwords.
- Never share your passwords with anyone, not even close friends or family.
- Use a password manager to securely store and manage your passwords.
- Regularly review your passwords and change them if you suspect they may have been compromised.
#PasswordSecurity #PasswordPolicy #Cybersecurity #PasswordTips #PasswordManagement #OnlineSecurity #DigitalDefense #PhishingAttacks #DataBreaches #StrongPasswords