Data Leakage: Understanding the Silent Threat to Your Information
December 31, 2024
Zero-Day Vulnerabilities: The Unknown Threats Lurking in Your Systems
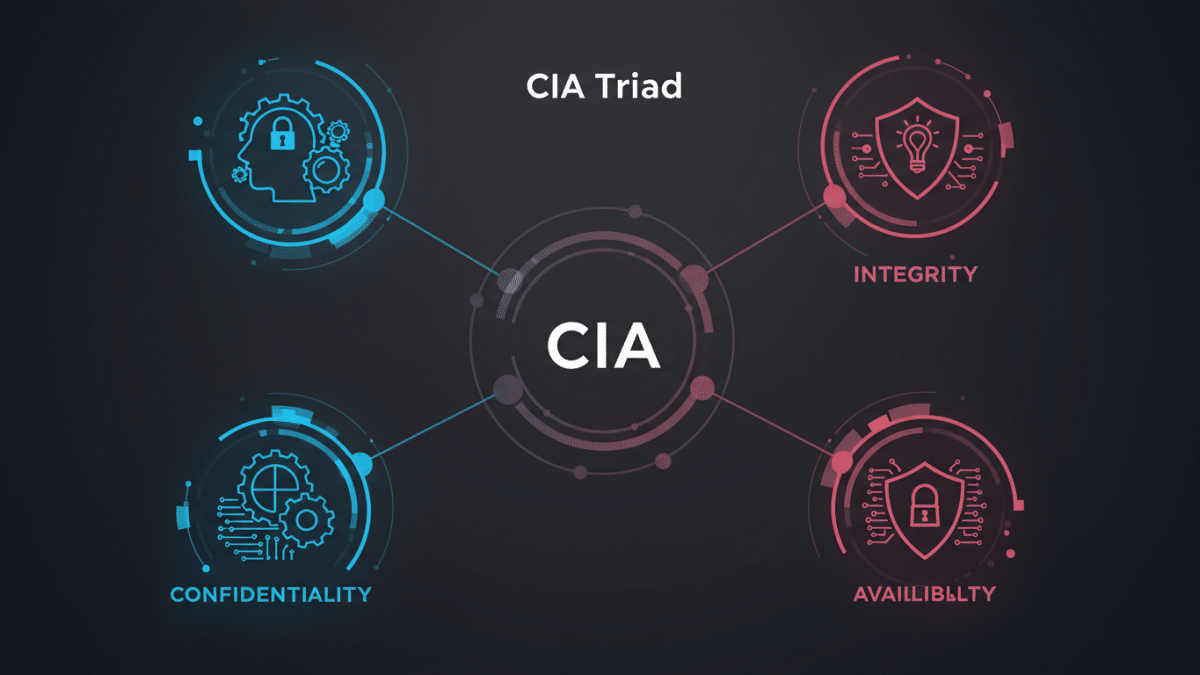
January 3, 2025In the complex world of cybersecurity, the CIA triad stands as a fundamental guiding principle. It represents the three core objectives of information security: Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. Understanding and implementing the CIA triad is essential for any organization seeking to protect its valuable data and systems.
As your trusted cybersecurity partner, Krypto IT is committed to demystifying key security concepts. This blog post will delve into each element of the CIA triad, explaining its importance and providing practical guidance on how to achieve it.
1. Confidentiality: Protecting Data from Unauthorized Access
What is Confidentiality?
Confidentiality is the principle of ensuring that sensitive information is accessible only to authorized individuals. It’s about preventing unauthorized disclosure or exposure of data, whether it’s personal information, financial records, intellectual property, or any other type of confidential data.
Why is Confidentiality Important?
- Protects Privacy: Safeguards personal information from falling into the wrong hands.
- Prevents Data Breaches: Reduces the risk of data breaches and their associated consequences.
- Maintains Competitive Advantage: Protects trade secrets and other confidential business information.
- Ensures Compliance: Helps organizations comply with data protection regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
Best Practices for Ensuring Confidentiality:
- Access Control:
- Principle of Least Privilege: Grant users only the minimum access necessary to perform their job duties.
- Strong Authentication: Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) to verify user identities.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Assign permissions based on user roles within the organization.
- Data Encryption:
- Encryption at Rest: Encrypt sensitive data stored on devices, servers, and in the cloud.
- Encryption in Transit: Use secure protocols (e.g., HTTPS, TLS/SSL) to encrypt data transmitted over networks.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP):
- Implement DLP solutions to monitor and control the flow of sensitive data, preventing unauthorized transfers or disclosures.
- Secure Data Disposal:
- Properly sanitize or destroy storage media before disposal or reuse.
- Use secure methods to dispose of physical documents containing confidential information.
- Employee Training:
- Educate employees about the importance of confidentiality, data protection policies, and secure data handling practices.
2. Integrity: Maintaining Data Accuracy and Trustworthiness
What is Integrity?
Integrity refers to the accuracy, completeness, and consistency of data over its entire lifecycle. It means ensuring that data has not been tampered with, altered, or destroyed in an unauthorized manner.
Why is Integrity Important?
- Data Reliability: Ensures that data is trustworthy and can be relied upon for decision-making.
- Error Prevention: Prevents accidental or intentional modification of data that could lead to errors or inconsistencies.
- Fraud Prevention: Makes it more difficult for attackers to manipulate data for fraudulent purposes.
- Compliance: Many regulations require organizations to maintain the integrity of certain types of data.
Best Practices for Ensuring Integrity:
- Hashing:
- Use cryptographic hash functions to generate unique fingerprints of data, allowing for verification of data integrity.
- Digital Signatures:
- Employ digital signatures to verify the authenticity and integrity of documents and messages.
- Version Control:
- Implement version control systems to track changes to data and allow for rollback to previous versions if necessary.
- Data Validation:
- Implement input validation checks to prevent invalid or malicious data from being entered into systems.
- Regular Backups:
- Create regular backups of critical data to ensure that a clean and accurate copy is available in case of data corruption or loss.
- Audit Trails:
- Maintain audit logs to track all changes made to data, including who made the changes and when.
3. Availability: Ensuring Reliable Access to Data and Systems
What is Availability?
Availability refers to the principle that authorized users should have timely and reliable access to information and systems when they need it. It’s about ensuring that systems are operational and that data is accessible to those who require it.
Why is Availability Important?
- Business Continuity: Ensures that business operations can continue uninterrupted in the event of system outages or disruptions.
- Productivity: Allows employees to access the data and systems they need to perform their jobs effectively.
- Customer Satisfaction: Ensures that customers can access services and information when they need them.
- Meeting Service Level Agreements (SLAs): Helps organizations meet their contractual obligations to provide a certain level of service availability.
Best Practices for Ensuring Availability:
- Redundancy:
- Implement redundant systems and infrastructure to eliminate single points of failure. This might involve having backup servers, redundant network connections, or geographically dispersed data centers.
- Disaster Recovery Planning:
- Develop and regularly test a disaster recovery plan to ensure that systems and data can be restored quickly in the event of a major outage.
- Load Balancing:
- Distribute network traffic across multiple servers to prevent overload and ensure high availability.
- Regular Maintenance:
- Perform regular system maintenance, including patching and updates, to prevent downtime and security vulnerabilities.
- Monitoring:
- Continuously monitor system performance and availability to detect and address potential issues proactively.
- Denial-of-Service (DoS) Protection:
- Implement measures to mitigate the risk of DoS attacks, which can disrupt service availability.
Policies and Procedures:
Implementing the CIA triad effectively requires clear policies and procedures. These should include:
- Data Classification Policy: Define different levels of data sensitivity (e.g., public, internal, confidential, restricted) and specify appropriate handling procedures for each level.
- Access Control Policy: Outline the principles of least privilege and role-based access control, and specify procedures for granting, reviewing, and revoking access.
- Incident Response Plan: Detail procedures for responding to security incidents that could compromise confidentiality, integrity, or availability.
- Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery Plans: Define procedures for maintaining business operations and recovering from disruptive events.
- Acceptable Use Policy: Outline acceptable use of company resources, including guidelines for handling sensitive data and protecting passwords.
Krypto IT: Your Partner in Achieving CIA
The CIA triad is a cornerstone of information security, and achieving it requires a holistic approach that encompasses technology, processes, and people.
Krypto IT can help your organization implement the CIA triad effectively. Our services include security assessments, policy development, security awareness training, technology implementation, and ongoing security monitoring. Contact us today for a free consultation and let us help you build a robust security posture that protects your valuable assets.
Don’t compromise on security. Prioritize Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. Partner with Krypto IT.
#Cybersecurity #CIATriad #Confidentiality #Integrity #Availability #InfoSec #DataSecurity #DataProtection #CyberDefense #RiskManagement #InformationSecurity #KryptoIT #SecurityBestPractices #CyberAwareness #TechSecurity